
Source: Indian express
- High-level trade talks are scheduled between the United States and China in London on Monday, June 10, 2025.
- This meeting marks a significant diplomatic effort to resolve ongoing trade tensions between the world’s two largest economies.
- From the US:
- US Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent
- Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick
- Trade Representative Jamieson Greer
- From China:
- Vice Premier He Lifeng (in the UK from June 8–13)
- From the US:
Purpose of the Talks
- To revive the China-US Economic and Trade Consultation Mechanism.
- Address long-standing disputes over trade imbalances, tariffs, and particularly the control over critical mineral exports (like rare earth minerals).
- Ease global economic uncertainties that have resulted from these tensions.
Recent Developments
- President Trump made the announcement via Truth Social.
- He held a rare phone call with President Xi Jinping ahead of the meeting, emphasizing diplomatic dialogue.
- Both countries are under economic pressure to reach common ground, especially due to supply chain risks and mineral resource dependence.
Significance
- A successful meeting could:
- Stabilize global markets and reduce volatility.
- Enhance bilateral cooperation in trade and investment.
- Impact global supply chains, especially in high-tech and green energy sectors dependent on rare earths.
- A failed dialogue may escalate trade wars, disrupt international trade, and affect countries reliant on both powers.
- A successful meeting could:
Where are the upcoming trade talks between the US and China scheduled to take place?
- Washington
B. Beijing
C. London
D. Geneva
Answer: C. London
The talks are set to take place in London as announced by US officials and reported in the article.
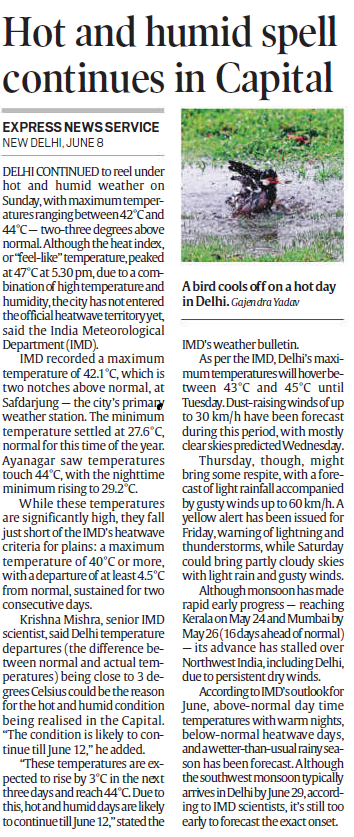
Delhi is currently facing an intense hot and humid spell with maximum temperatures 2–3°C above normal, alongside delayed monsoon progression in Northwest India. The Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) has issued alerts and forecasts related to the heat, winds, and potential rainfall.
Temperature Data
- Maximum temperatures in Delhi: 42°C to 44°C
- “Feels-like” temperature peaked at 47°C
- IMD recorded:
- Max: 42.1°C at Safdarjung (2°C above normal)
- Min: 27.6°C (Safdarjung), 29.2°C (Ayanagar)
- Night temperatures remain significantly high
Heatwave Status
- Delhi has not officially entered heatwave territory.
- IMD’s heatwave criteria for plains:
- ≥40°C and
- ≥4.5°C above normal for two consecutive days
Which of the following conditions must be met for the India Meteorological Department (IMD) to declare a heatwave in the plains?
- Temperature ≥ 40°C and departure ≥ 4.5°C from normal for one day
B. Temperature ≥ 40°C and departure ≥ 4.5°C from normal for two consecutive days
C. Temperature ≥ 42°C and humidity above 70%
D. Night temperature above 30°C for three consecutive days
Answer: BAccording to IMD, for plains, a heatwave is declared when the maximum temperature reaches 40°C or more and is at least 4.5°C above normal for two consecutive days.

- India has successfully created its first gene-edited sheep, a Kashmir Merino breed, at the Embryo Biotechnology Lab of SKUAST-K, Srinagar.
- The sheep was born in December 2023, but the announcement was made in June 2025 after gene sequencing confirmed the success.
- This marks a pioneering achievement in Indian livestock gene-editing, comparable to global standards.
- Target Gene: Myostatin gene – a negative growth regulator.
- Purpose: Inhibiting this gene increases muscle mass (up to 30%) and improves meat quality.
- Technique Used: CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing – a precise and advanced genetic engineering tool.
- Outcome: The sheep showed significant weight gain (from 3.15 kg at birth) and healthy development under lab care.
- Target Gene: Myostatin gene – a negative growth regulator.
Key Institutions & Scientists Involved
- Lead Scientist: Prof. Riyaz Ahmad Shah, SKUAST-K
- Supporting team: Dr. Suhail Magray, Dr. Naresh Selokar (NDRI, Karnal), and others.
- Past Achievements:
- The same team produced India’s first cloned Pashmina goat “Noori” in 2012.
Why This is Important
|
|
|---|---|
Livestock Sector | Enhances muscle mass and meat yield in sheep |
Farmers’ Income | Potentially improves returns through quality livestock |
Disease Resistance | Paves way for developing disease- and climate-resistant breeds |
Biopharma Potential | Opens scope for producing medicinal proteins in animals (e.g. vaccines, insulin) |
Future Roadmap
- Focus now shifts to editing FGF5 gene to improve wool quality.
- Longer-term goals include:
- Developing animals that can withstand climate stress.
- Producing pharmaceutical-grade proteins in livestock.
Challenges
- Several failed attempts before successful editing.
- Ethical concerns and regulatory approvals remain significant hurdles.
India’s first gene-edited sheep was developed by which of the following institutions?
A) ICAR – National Dairy Research Institute, Karnal
B) Indian Veterinary Research Institute, Bareilly
C) SKUAST-K, Srinagar
D) National Institute of Animal Biotechnology, Hyderabad
Answer: C) SKUAST-K, Srinagar
The sheep was developed at the Embryo Biotechnology Lab of Sher-e-Kashmir University of Agricultural Sciences and Technology (SKUAST-K) in Srinagar.

External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar is on a week-long official visit (June 8–14) to France and Belgium.
Aim: Strengthen India’s diplomatic engagement with the European Union (EU) and deepen cooperation in various strategic areas.
Objectives of the Visit
- Part of India’s diplomatic campaign “Operation Sindoor” to:
- Garner support against terrorism.
- Reinforce strategic partnerships in Europe.
- Reaffirm India’s commitment to:
- Bilateral cooperation
- Trade negotiations
- Global and regional security issues
- Part of India’s diplomatic campaign “Operation Sindoor” to:
In France (Paris, Marseille)
- Bilateral talks with French Foreign Minister Jean Noel Barrot
- Addressing the “Mediterranean Raisina Dialogue” – joint forum by ORF and French institutions
- Marseille port considered for the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC)
(Note: IMEC’s future uncertain due to the Israel-Gaza conflict, but India is still pursuing it)
🇪🇺 In Belgium (Brussels)
- Strategic Dialogue with:
- EU High Representative & VP Kaja Kallas
- Belgian Deputy PM and Foreign Minister Maxime Prevot
- Strategic Dialogue with:
Agenda includes:
- India’s request for repatriation of Mehul Choksi (wanted for fraud and embezzlement)
- Progress on the India–EU Free Trade Agreement (FTA), targeted for conclusion by end of 2025
Strategic Importance
- Strengthens India’s strategic footprint in Europe
- Supports trade talks, especially post-Brexit re-engagement
- Reasserts India’s role in multilateral diplomacy, global economic corridors (IMEC)
- Key for India’s counter-terrorism diplomacy and diaspora-related legal concer
The term “Operation Sindoor” in the context of Indian diplomacy refers to:
A. India’s counter-terrorism operation on the Pakistan border
B. A health diplomacy campaign in Africa
C. A diplomatic push to gain international support against terrorism
D. An Indian Ocean naval exercise with ASEAN countries
Answer: C. A diplomatic push to gain international support against terrorism
Operation Sindoor is a diplomatic initiative to gather global backing for India’s stand against terrorism.

Andhra Pradesh is set to begin the first deployment of trained Kumki elephants (tamed tuskers) to manage wild elephant menace in Chittoor district.
- The operation aims to prevent crop damage, reduce human-elephant conflict, and ensure safer settlements near forests.
What are Kumki Elephants?
- Kumkis are trained captive elephants used in managing wild elephants, especially to:
- Control crop-raiding wild herds
- Rescue operations
- Wildlife tracking and tranquillizing
- Kumkis are trained captive elephants used in managing wild elephants, especially to:
Highlights of the Operation
- Location: Musalimadugu camp near Palamaner, Andhra Pradesh
- Elephants: 4 trained kumkis brought from Karnataka (1 still undergoing orientation)
- Initiative by: AP Deputy Chief Minister Pawan Kalyan
- Training Program: 30-day module to help elephants adjust to:
- Local terrain and topography
- Behavioural patterns of wild elephants
- Climatic conditions
Purpose of Operation
- Mitigate the rising elephant attacks in Chittoor district
- Prevent damage to standing crops like:
- Paddy
- Tomato
- Groundnut
- Reduce human and livestock casualties
- Significance
- Represents inter-state cooperation (Karnataka ➝ Andhra Pradesh)
- Reflects the increasing use of trained animal resources for:
- Conservation-linked conflict resolution
- Sustainable forest management
Which of the following best describes a “Kumki elephant”?
A. A wild elephant trained for circus performances
B. A domesticated elephant used for patrolling forest fires
C. A trained elephant used to manage wild elephant conflicts
D. A species of elephant endemic to the Eastern Ghats
Answer: C
Explanation: Kumki elephants are trained captive elephants used to drive away or manage wild elephants, especially in conflict zones.

- Indian courts are increasingly prioritizing sentiments over the protection of free speech, leading to a retreat from Article 19(1)(a) of the Constitution.
- The judiciary is often seen policing speech content, especially when it offends prevailing social or political sentiments.
- Editorial reflects on a series of court cases that illustrate a growing intolerance to dissent, criticism, or satire.
Case Examples
- Chittoor FIR Case (May 2025):
- A 24-year-old was arrested for criticizing PM Narendra Modi.
- The Allahabad High Court refused to quash the FIR and stated that “emotions cannot be permitted to override a constitutional discourse”.
- Raises concern over criminalization of dissent.
- Kamal Haasan’s film (Thevar Magan):
- Criticism faced for offending Tamil sentiments.
- Judiciary asked for an apology to “sentiments of the masses”.
- Prof. Ali Khan Mahmudabad Case:
- Faced trial for past critical views on India’s relations with Pakistan.
- Example of using legal proceedings to punish academic criticism.
- Rahul Gandhi Case:
- Held guilty of defamation over a political remark made about a community.
- Reflects misuse of defamation laws to stifle political speech.
- Usage of IPC Sections 124A, 153A, 295A, etc.:
- These are frequently used to punish speech that “hurts sentiments”, despite lacking the “clear and present danger” test.
Concerns Highlighted
- Judicial Overreach: Courts are interpreting laws based on emotional appeal, not constitutional principles.
- Rise of Subjective Standards: Courts are increasingly encouraging “outrage policing”, where personal hurt becomes grounds for prosecution.
- Impact on Democracy: When speech is judged on agreeability rather than legality, it chokes critical discourse and dissent.
- Misreading Article 19(2): Restrictions on speech are supposed to be reasonable, not based on subjective hurt or outrage.
Important Constitutional Angle
- Article 19(1)(a): Guarantees the freedom of speech and expression.
- Article 19(2): Allows for reasonable restrictions, but only on limited grounds: sovereignty, security, decency, morality, etc.
- Concern: Courts expanding “reasonable restrictions” to include subjective hurt sentiments is against constitutional spirit.
Article 19(2) of the Indian Constitution allows reasonable restrictions on freedom of speech on all the following grounds EXCEPT:
A. Decency or morality
B. Friendly relations with foreign States
C. Offending religious sentiments
D. Public order
Answer: C
“Offending religious sentiments” is not an explicit ground under Article 19(2); restrictions must be based on defined grounds like public order, morality, etc.

India is currently engaged in trade negotiations with the United States, focusing especially on agricultural market access. Union Agriculture Minister Shivraj Singh Chouhan emphasized that protecting farmers’ interests will be India’s top priority during the talks.
- India will not open domestic markets unless the interests of its farmers are fully safeguarded.
- The negotiations are part of the first phase of the bilateral trade deal, expected to be signed by September–October 2025.
- Talks are focused on balancing trade-offs between U.S. demands for access to Indian markets and India’s commitment to rural livelihoods and food security.
U.S. Trade Demands
- The U.S. seeks greater market access for its agricultural and horticultural products.
- It wants to export more pulses, soybeans, corn, and animal feed to India.
- However, it faces high tariffs, especially in agriculture (average tariffs in India are between 39% to 50%).
India’s Position
- India exported $2.22 billion worth of agricultural and allied goods to the U.S. during the triennium ending 2024.
- The U.S. exported around $5.75 billion worth of agricultural goods to India in the same period.
- India is cautious about lowering tariffs due to:
- Price volatility in global markets.
- Rural community backlash.
- Protecting domestic food production and farmers.
NITI Aayog Recommendation
- A NITI Aayog report on “Promoting India-U.S. Agricultural Trade” suggests careful consideration of the new U.S. trade regime.
- India must weigh gains vs. losses before finalizing any agreement.
What is India’s top priority in its ongoing trade negotiations with the United States, as per Union Agriculture Minister Shivraj Singh Chouhan?
A. Increasing exports of Indian dairy products
B. Ensuring market access for Indian textiles
C. Protecting the interests of Indian farmers
D. Promoting IT services in the U.S. market
Answer: C. Protecting the interests of Indian farmers
India aims to protect farmers before agreeing to any agricultural market access demands from the U.S.

A new study published in the journal Earth’s Future has presented a more viable approach to Stratospheric Aerosol Injection (SAI), a controversial technique proposed for climate control by reflecting solar radiation away from Earth.
What is Stratospheric Aerosol Injection (SAI)?
- SAI involves injecting aerosols (like sulphur particles) into the stratosphere (~20 km altitude) to reduce sunlight reaching Earth’s surface, thus cooling the planet.
- Inspired by volcanic eruptions like Mount Pinatubo (1991), which temporarily cooled Earth after injecting particles into the atmosphere.
How it works
SAI increases atmospheric reflectivity:
- Aerosols form reflective clouds that scatter sunlight.
- These particles absorb and re-emit longwave radiation, reducing surface temperatures.
Study Findings
- SAI is more feasible than earlier believed if the injection is done directly above the tropics.
- New modelling suggests just 7.6 million tonnes of aerosols per year injected at higher altitudes can significantly reduce temperatures.
- Lower altitudes or different latitudes would require up to five times more material.
Concerns & Challenges
- Global Impact: Effects of SAI are not limited to one country – could lead to international conflicts.
- Ozone layer depletion and stratospheric warming.
- Moral hazard: May reduce urgency to cut carbon emissions.
- Unequal regional effects: Some regions could face reduced rainfall, drought, or crop loss.
Solar Climate Intervention Methods (From Infographic in Article)
- Surface albedo enhancement
- Marine cloud brightening (MCB)
- Stratospheric Aerosol Injection (SAI)
- Space-based reflectors
- Cirrus cloud thinning
Governance and Policy Implications
- No international legal framework currently governs SAI.
- Calls for a UN-led regulation mechanism.
- U.S. government has resumed funding of geoengineering research under pressure from climate urgency.
What is the main objective of Stratospheric Aerosol Injection (SAI)?
A. Increase atmospheric oxygen levels
B. Reduce greenhouse gas concentration
C. Reflect sunlight to reduce global warming
D. Stimulate rainfall in arid regions
Answer: C. Reflect sunlight to reduce global warming
SAI injects aerosols into the stratosphere to reflect sunlight and reduce surface temperatures.
